Exploring Halogen Bonds in 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2B Receptor–Ligand Interactions
Yu Zhou†#, Yuanxun Wang‡†#, Pengfei Li†, Xi-Ping Huang§, Xiangbin Qi†∥ , Yunfei Du*‡ , and Niu Huang*†∥
† National Institute of Biological Sciences, Beijing 102206, China
‡ School of Pharmaceutical Science and Technology, Tianjin University, Tianjin 300072, China
§ Department of Pharmacology, The National Institute of Mental Health Psychoactive Drug Screening Program (NIMH-PDSP), The University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina 27759, United States
∥ Tsinghua Institute of Multidisciplinary Biomedical Research, Tsinghua University, Beijing 102206, China
Abstract
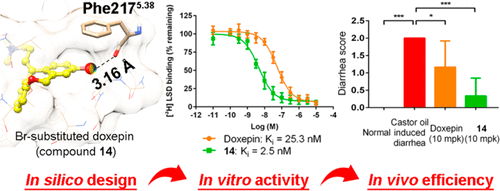
Here, we predicted the potential halogen bonding interaction between compound 2 and the 5-hydroxytryptamine 2B (5-HT2B) receptor and systematically assessed this interaction via structure–activity relationship analysis and molecular dynamics simulations. A physics-based computational protocol was then developed to further explore the opportunity of “designing in” halogen bonding interactions in structure-based ligand design for the 5-HT2B receptor, which not only facilitated the identification of previously uncharacterized halogen bonds in known 5-HT2B ligands but also enabled the rational design of halogen bonding interactions for the optimization of 5-HT2B ligands. As a proof-of-concept, a series of halogen-substituted analogues of doxepin was synthesized and evaluated, which showed improved in vitro and in vivo potency.
